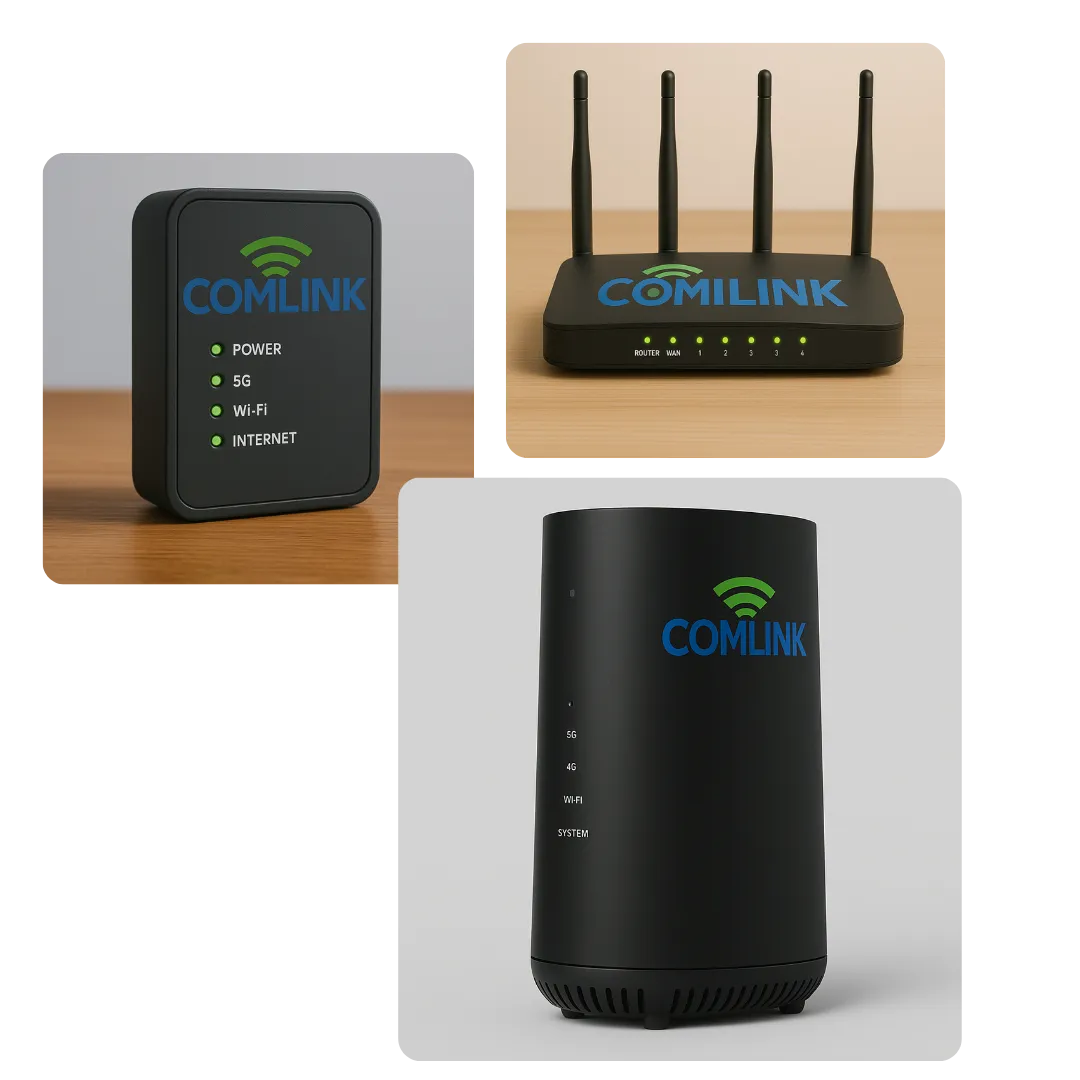
Unlimited High-Speed Wireless for Every Home
“Stay Connected Anywhere with Comlink LTE – No Limits!
Comlink Internet Best Deals On Internet Services!
Searching for an internet or TV provider can be hectic.
Contact Us, and we will guide you about the best feasible options according to your zip code.
High-Speed Connectivity Where You Need It Most Looking for internet providers near me
that offer reliability, flexibility, and lightning-fast speeds? At Comlink Internet, we bring you the
best internet plans tailored to your lifestyle—whether you're working from home, gaming, streaming, or staying connected on the go.
Key Features

Unlimited DATA!
Comlink offers truly unlimited data plans, allowing users to stream, browse, and download without worrying about data caps or speed reductions.

No Credit Checks
Enjoy the flexibility of Comlink's services with no credit checks, or, making it accessible for a wide range of customers.

High-Speed Connectivity
With download speeds of up to 500 Mbps, Comlink's LTE internet supports high-bandwidth activities like HD streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing.
Easy Installation and Setup
Comlink utilizes fixed wireless technology through cellular towers, ensuring quick and straightforward setup without the need for extensive infrastructure.

Ideal for Rural Areas
Comlink specializes in providing high-speed internet to rural areas where traditional broadband options may be limited, ensuring reliable connectivity for underserved communities.

Flexible Plans
Comlink offers multiple LTE internet plans to cater to varying user needs. Customers can choose between plans offering download speeds of up to 25 Mbps or 500 Mbps.

Trusted Industry Presence
Proven Track Record in Rural Connectivity
Comlink is especially well-known for providing unlimited high-speed internet in rural areas, utilizing fixed wireless technology through cellular towers to ensure consistent service where traditional broadband options may be limited.
Accessible to all major Carrier Towers, At&t, Verizon, T-Mobile etc;
Enter your ZIP code to view accurate, localized pricing, availability, speeds, and bundle options.
Comlink Internet is your go-to resource for simplifying the search for Internet, TV, and mobile phone services
🧰 All-in-One Convenience
Instead of visiting multiple provider websites or calling around, you can
Unlimited LTE Internet , wireless internet with no data caps
Easily add TV and streaming services
Get expert assistance
Complete sign-ups online

Comlink INTERNET 4G/5G Packages

ESSENTIALS
25 Mbps Download Speed
Internet with Ultra-Low Latency
Fast & Reliable Internet
Free Modem & Antivirus: with 2 year agreement
Bundled Savings

ELITE
50 Mbps Download Speed
Internet with Ultra-Low Latency
Fast & Reliable Internet
Free Modem & Antivirus: with 2 year agreement
Bundled Savings

PREMIER
100 Mbps Download Speed
Internet with Ultra-Low Latency
Fast & Reliable Internet
Free Modem & Antivirus: with 2 year agreement
Bundled Savings
ULTIMATE INTERNET 5G Packages

ULTIMATE
5G SPEED
250 Mbps Download Speed
Internet with Ultra-Low Latency
Free Modem & Antivirus: with 2 year agreement
Bundled Savings:
Not available in all areas

ULTIMATE PLUS
5G SPEED
500 Mbps Download Speed
Enhanced WiFi Experience
Internet with Ultra-Low Latency
Bundled Savings:
Not available in all areas
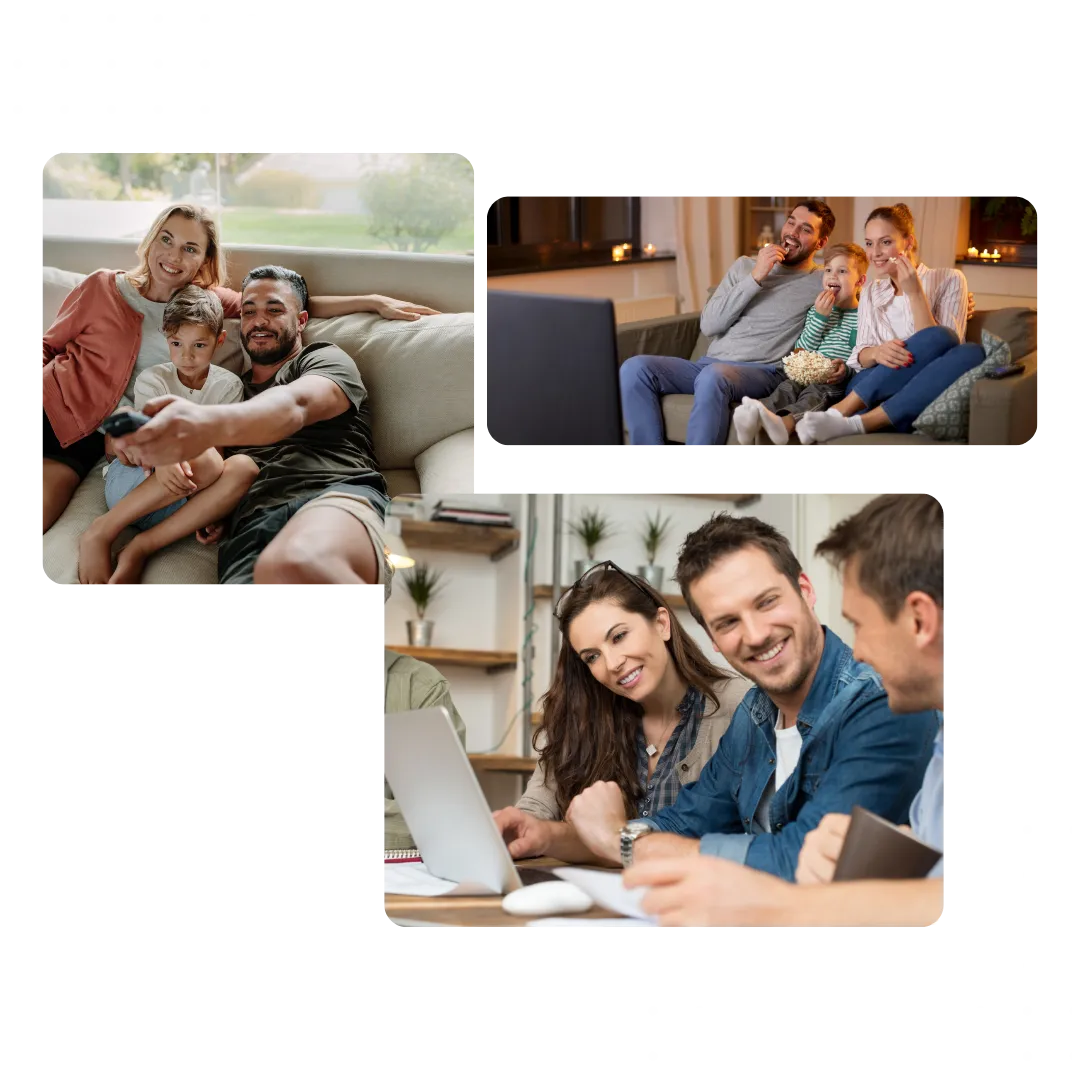
Hear what our customers have to say.
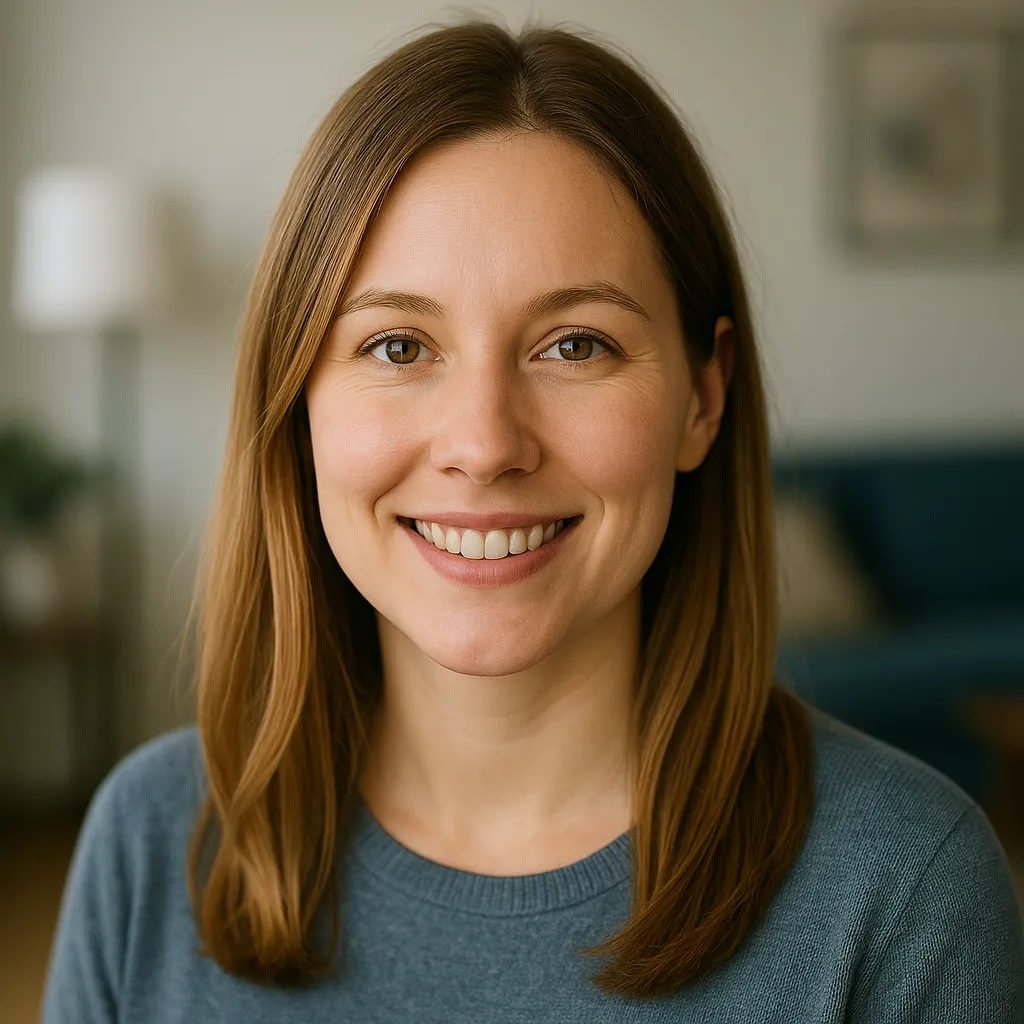

"We struggled for years with slow satellite internet. Switching to Comlink Internet was a game-changer. The speeds are amazing, and we’ve had zero issues streaming, working from home, or the kids gaming. Highly recommend!”
Jennifer M.
Fort Myers, FL
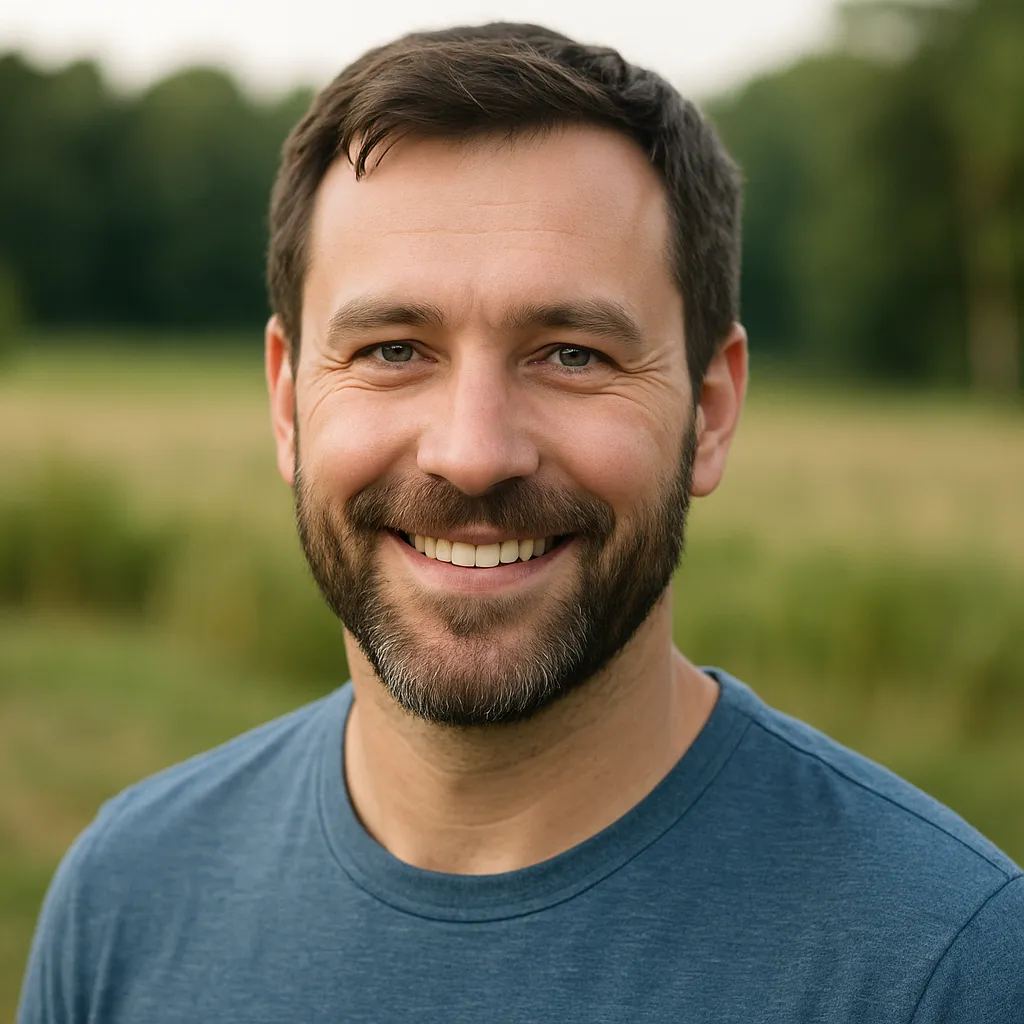


"I love that Comlink doesn’t run a credit check. Setup was super easy, and the unlimited data plan gives me peace of mind. Best decision we’ve made!
Jeff S.
Austin, TX
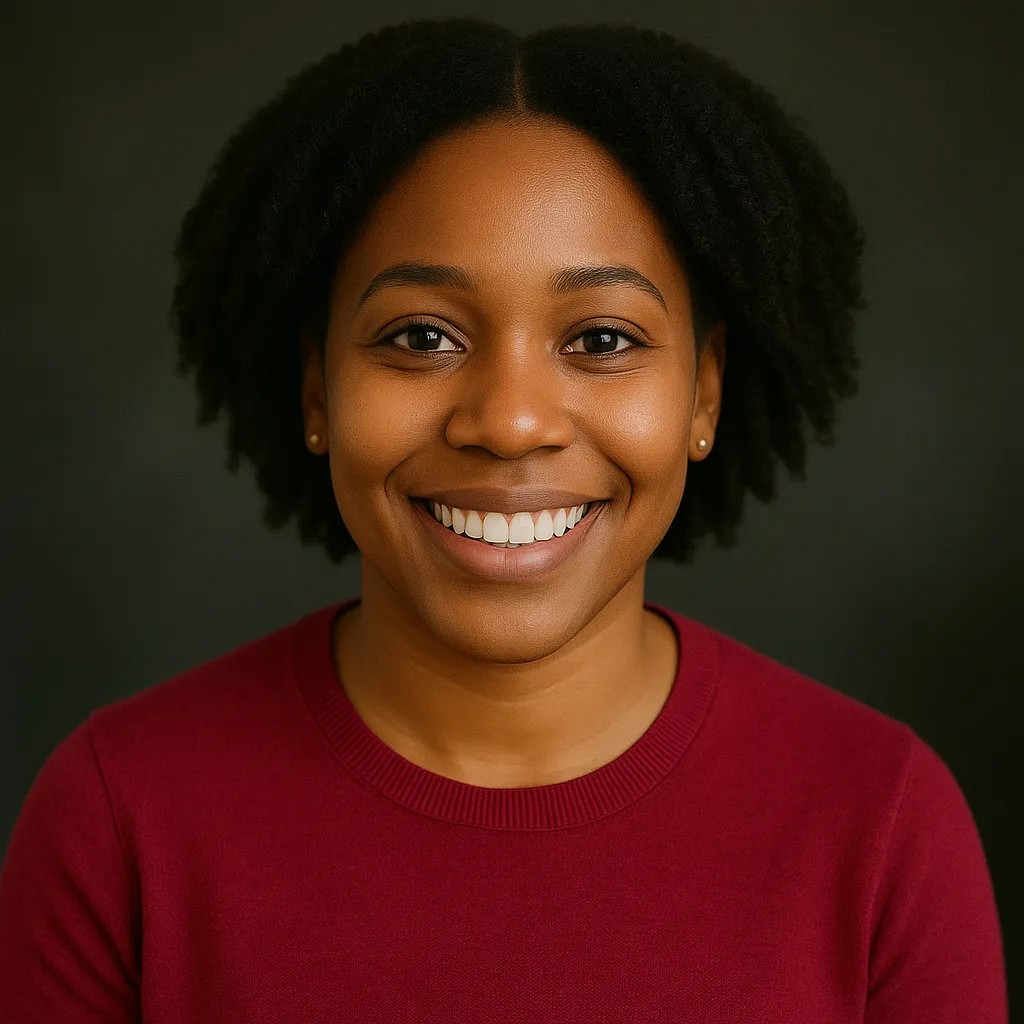


"We needed reliable internet to run our shop's POS and security system, and Comlink delivered. Speeds are fast and stable, and the included phone service is a bonus. Couldn’t be happier."
Jazmine C.
Denver, CO

Home WiFi That Works as Hard as You Do
Our home WiFi solutions are designed for seamless coverage and ultra-fast connections in every room. Say goodbye to dead zones and hello to uninterrupted video calls, streaming, and smart home control.
High-Speed Internet. Everywhere.
Need high speed internet in a rural area or on the move? We offer mobile internet options that keep you connected no matter where life takes you. From RV travelers to remote workers, Comlink makes reliable internet possible—anywhere.
Fiber Internet Alternative
Experience blazing-fast downloads and minimal lag with just like fiber internet with our 5G plans available in select areas. Perfect for gamers, streamers, and households with multiple devices online at once.
Better Than T-Mobile/Verizon Home Internet?
Searching for T-Mobile or Verizon home internet
Comlink outperforms with dedicated customer service, wider availability, and customizable options built for your needs since we work on all carrier networks!
Don't worry, we can help!
Frequently Asked Questions
What services does Comlink Internet Provide?
We provide Fixed Wireless 4G and 5G service and are an authorized dealer for top telecom providers in USA. The website lets you view and order all the applicable offers from local phone, cable, and internet providers in your area.
Who are the best Internet, Cable, Phone and TV Providers?
Your location and the availability of the supplier will determine the answer. Find out which phone, cable, and internet service providers are available in your area by running your complete street address on our website. You can also talk to us at 866-261-2148.
What is this best internet provider for rural areas?
Many rural locations are served by Xfinity and CenturyLink, but if you live in a remote location, your only alternatives for internet connectivity may be satellite internet from Viasat or HughesNet or fixed wireless internet service from Comlink Internet.
Do you offer 5G Internet plans?
Yes we offer many 5G internet plans from multiple providers like At&t,Verizon T-Mobile and our brand called Comlink Internet.
Why Choose Comlink?
✅ Reliable service in urban, suburban, and rural areas
✅ The best internet plans for every budget
✅ Industry-leading technology & support
✅ Seamless setup with no credit checksLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.


📍 Nationwide Coverage
No matter where you live, Comlinkinternet.com works with leading national and regional providers to show you the best options available in your exact location..
Innovative Tools: Transform telecom with our cutting-edge AI features.
Stream lining : Save time and and money with search engine.
🏢 National Internet Providers (Wired & Fiber)
Provider
Service Type
Coverage & Notes
Xfinity
AT&T
Spectrum
Verizon Fios
Frontier
Cox
Optimum
CenturyLink
Mediacom
WOW!
RCN / Astound
EarthLink
Comlink
Cable
Cable
Cable
Cable
DSL, Fiber
Cable
Cable, Fiber
DSL, Fiber
Cable
Cable
Cable, Fiber
DSL, Fiber (Reseller)
Fixed Wireless (Reseller)
Widest U.S. coverage
Fiber available in select areas
Suburban & urban coverage
Northeast & select cities
Expanding rural fiber footprint
Strong in the South and Southwest
Northeast & parts of California
Wide DSL coverage, limited fiber
Midwest & South
Midwest, Southeast
Urban NYC, Chicago, etc.)
Nationwide via partnerships
Nationwide via partnerships
COMPANY
CUSTOMER CARE
NEWS
LEGAL

© Copyright 2025. Comlink . All Rights Reserved.
